Sense and Perception
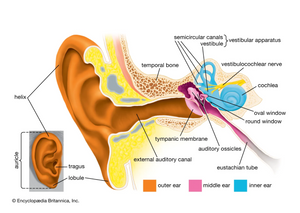

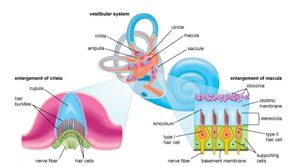
The primary sense organs of touch and movement are located throughout the body—in every Cell. Touch is emphasized in the Skin, and Movement is emphasized in the proprioceptive and kinesthetic receptors in the joints, ligaments, muscles, and tendons, the interoceptors of the organs, and the vestibular mechanism of the inner ear.
"Sense and perception the school of body-mind Centering"
The difference between Proprioceptive and kinesthetic
The literature is often divergent, with some considering proprioception as an inclusive sense containing both the kinesthesis and vestibular systems, while others consider them as two separate senses with proprioception as part of the balance sense (along with vision and the vestibular system) and the kinesthetic sense as related to movements. What is convergent is that proprioception informs us about where our body is positioned in space and kinesthesia provides useful information on how we move in space. Another important distinction is that proprioception is more related to our awareness of our body and therefore is often used to describe the cognitive component of the sense; while kinesthesia is related to the behavioral component of the sense.
link to reference
Task: Look at the different planes with movement.
Vestibular system - postural (body)tone, balance, equilibrium function position in space, movement through space, relationship of body parts to each other, relationships to gravitational pull and fluid pressure, changes in velocity, patterns of movement sequencing, movement of our environment, and social contact and communication. It receives information from all the cells in the body
One of the first special sense in the head to delveope and it develops through close association with touch
\\Skin layers
pleasure and displeasure, vibrations, touch, pressure, temperature and social contact and communication
Epidermis top layer
- protective layer
- Makes new skin
- Protects your body
Dermis (middle layer) collagen cells
- flexible
- keep the skin shape.
- nerves detect heat, soft itchy
- hair follicles
- sweat
- oil to protect your skin from becoming to dry or in rain or swimming
Hypodermis (bottom layer of skin)
- cushion muscles and bones - fat in the hypodermis
- Has connective tissue, which connects layers of the skin to muscles and bones
- regulates body temperature
TASK move from the skin
link to reference page